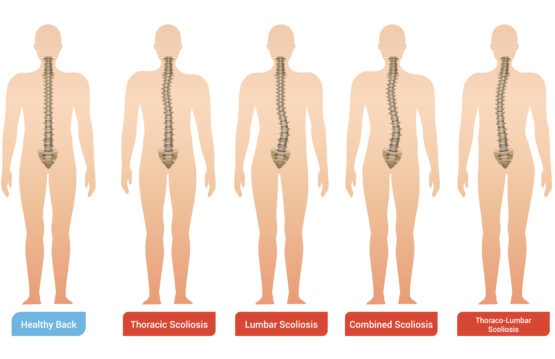
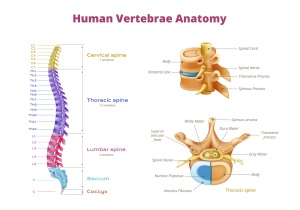
Scoliosis in adults is a condition of the spine characterized by its lateral deviation in the shape of “S” or “C”. Although we often associate this problem with adolescence, scoliosis can also affect adults, often going unnoticed or neglected.
In this article, we’ll explore five lesser-known aspects of scoliosis in adults, highlighting the importance of awareness and management of the condition.
CONTENT:
- Scoliosis doesn’t stop at adolescence
- Pain is not the only symptom of scoliosis in adults
- Early and correct diagnosis of scoliosis in adults is essential
- Treatment is not just limited to surgery
- Mindset and psychological support are important for adult scoliosis sufferers
Scoliosis doesn’t stop at adolescence
Scoliosis, although frequently associated with adolescence, is not a problem that stops at this stage of life. Contrary to common belief, many adults can develop or experience a progression of scoliosis even after adolescence. There are several reasons for this development, namely missed diagnosis in childhood, injuries, vertebral degeneration and changes associated with the aging process.
One of the main factors contributing to the persistence or onset of scoliosis in adults is missed diagnosis in childhood. Sometimes scoliosis can be underdiagnosed or even overlooked during the period of rapid growth. A child may have a slight deviation of the spine, and this problem may remain undiagnosed or uncorrected, evolving into a more pronounced scoliosis in adult life.
In addition to missed diagnosis, injuries are another important factor in the development of scoliosis in adults. Accidents, falls, or trauma experienced during life can affect the spine and contribute to the development or worsening of scoliosis. Injuries can disrupt the normal alignment of the spine and lead to deformities that progress over time.
Vertebral degeneration, a natural consequence of the aging process, can also contribute to the development of scoliosis in adults. As the intervertebral discs deteriorate and the vertebrae lose bone density, deformities and misalignments can occur in the spine. These aging-related changes may contribute to the progression of scoliosis and associated symptoms.
Aging-related changes are not limited to bone degeneration, but can also include changes in the soft tissues that support the spine. The muscles and ligaments that keep the spine stable can become weaker and less elastic, which can promote the progression of scoliosis.
Pain is not the only symptom of scoliosis in adults
Pain, although a predominant symptom associated with scoliosis in adults, is not the only sign of this condition. Scoliosis can have a wide range of manifestations, and understanding them can be crucial to the correct diagnosis and management of the disease.
- Fatigue in the affected part of the spine
This is another significant symptom of scoliosis in adults. Throughout the day, people with scoliosis may experience excessive fatigue in the muscles required by the spinal deviation. This fatigue can occur as a result of the extra effort required to maintain the correct body position or to compensate for imbalances caused by the deviation of the spine.
- Muscle weakness
It is another important aspect of scoliosis in adults. The musculature around the spine can undergo changes in structure and function due to the misalignment, leading to loss of muscle strength and tone. This can affect the person’s ability to support the spine effectively and contribute to the discomfort and deformities associated with scoliosis.
- Posture changes
It is also a common sign of scoliosis in adults. As the spine deviates laterally, the overall body position can undergo significant changes. These changes can affect both standing and sitting positions, impacting not only the aesthetic appearance but also the functionality of the body in daily activities.
- Dysfunctions of internal organs
These are serious consequences of severe scoliosis in adults. For example, a pronounced scoliosis can affect the ability of the lungs to expand properly, which can lead to breathing problems. Compression or displacement of internal organs from their normal position can affect their functionality and generate specific symptoms such as breathing difficulties or digestive dysfunctions.
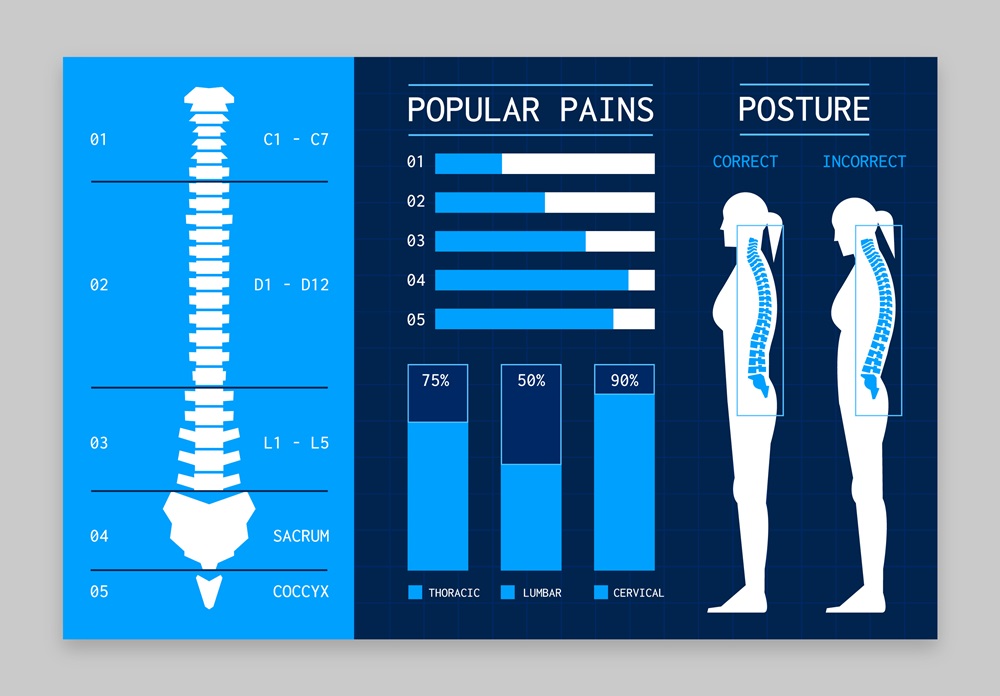
Early and correct diagnosis of scoliosis in adults is essential
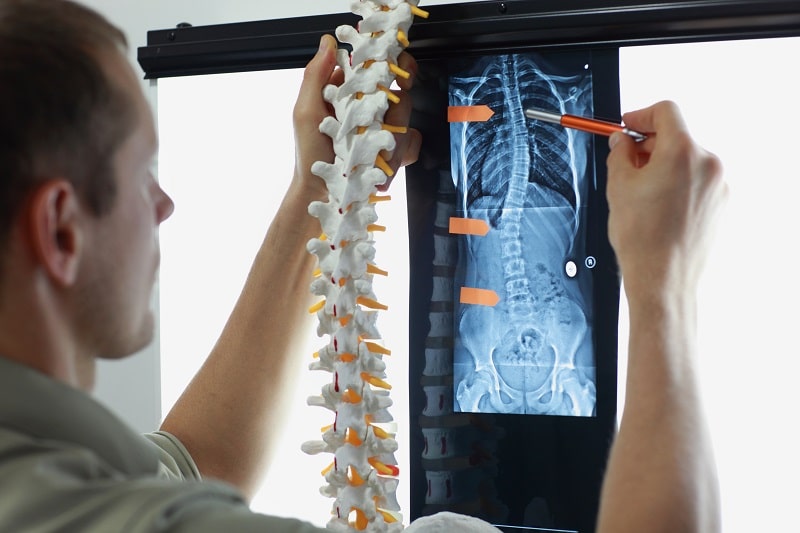
Early diagnosis of scoliosis in adults is essential for effective management of the condition. However, because symptoms can vary and scoliosis can progress slowly, many adults may not be aware of the problem. Doctors often need medical imaging, like X-rays and CT scans, to identify and assess the degree of scoliosis.
Consultation with an orthopedic specialist or physiatrist is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and establishing an appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment is not just limited to surgery
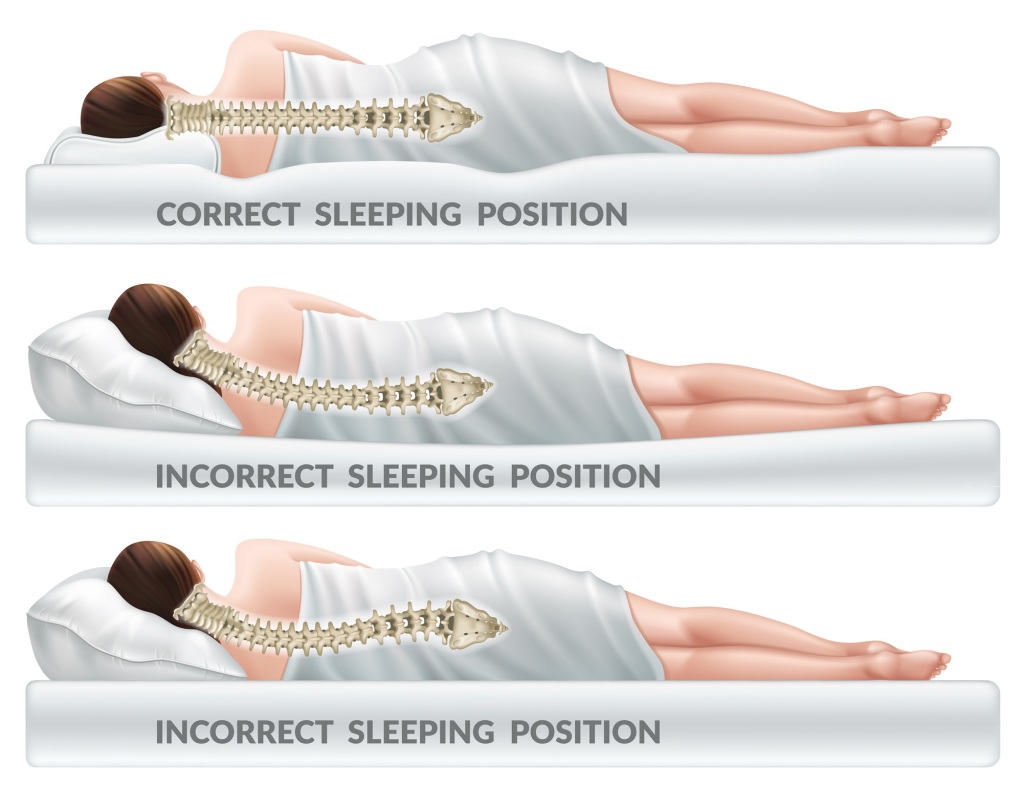
Many adults dread the idea of surgery to treat scoliosis, but there are a wide range of treatment options available. Physiotherapy and personalized exercise can help relieve symptoms and strengthen the muscles of the spine.
Postural control techniques and wearing orthotic braces can also help manage scoliosis. Even in severe cases, surgery is a viable option and may be necessary to correct deformities and prevent further complications.
Mindset and psychological support are important for adult scoliosis sufferers
Scoliosis can affect not only the physical body, but also a person’s psychological well-being. It is important to recognize the psychological impact of scoliosis and provide emotional support to those affected. Adults with this disease may benefit from psychological counseling or support groups that share experiences and strategies for managing the condition.
In conclusion, scoliosis in adults is an underestimated condition, but awareness and management of it can make a significant difference in quality of life. Ongoing education, early diagnosis, and varied therapeutic options are key to a comprehensive approach to this complex spinal condition.